Balance Sheet Example Template Format Analysis Explanation
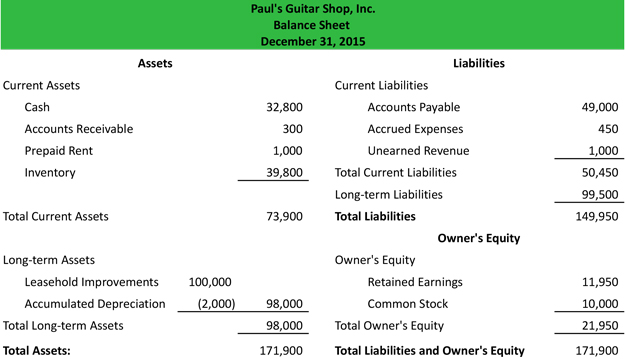
It’s important to note that the balance sheet should always balance. However, there are instances where it might not because a mistake has been made in the process. If your balance sheet doesn’t balance, you should double-check your data and calculations. Lenders will want to verify that you are able to pay back your debts.
Importance of balance sheets and how to use them
After you have assets and liabilities, calculating shareholders’ equity is done by taking the total value of assets and subtracting the total value of liabilities. You will need to tally up all your assets of the company on the balance sheet as of that date. For instance, if a company takes out a ten-year, $8,000 loan from a bank, the assets of the company will increase by $8,000. Its liabilities will also increase by $8,000, balancing the two sides of the accounting equation. You can calculate total equity by subtracting liabilities from your company’s total assets.
Current liabilities
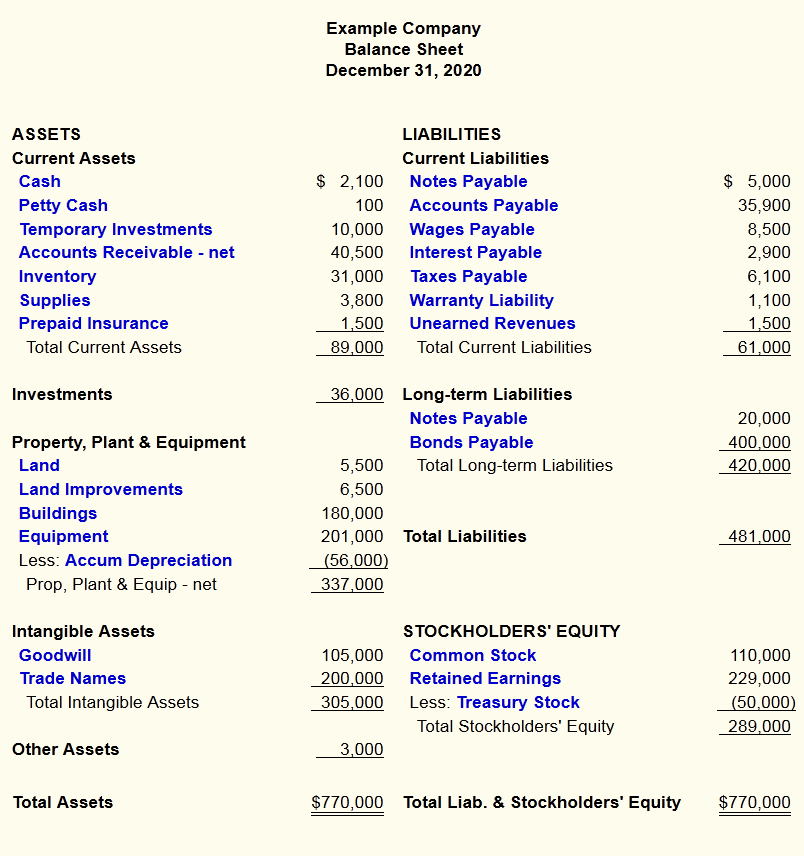
It’s important to note that this balance sheet example is formatted according to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which companies outside the United States follow. If this balance sheet were from a US company, it would adhere to Generally Accepted xero for small business Accounting Principles (GAAP). Current and non-current assets should both be subtotaled, and then totaled together. An asset is anything a company owns which holds some amount of quantifiable value, meaning that it could be liquidated and turned to cash.
The hassle-free international business account.
Not only will you need to know this figure, but potential buyers will want to know—and have the proof to back it up. A balance sheet must always balance; therefore, this equation should always be true. The column of amounts that is closest tothe words will be the most recent amounts.
- It’s wise to have a buffer between your current assets and liabilities to at least cover your short-term financial obligations.
- To find out which is the right option for your business, check out our article detailing the best accounting software for small businesses.
- The accounting balance sheet gives an overview of the company’s assets, while the functional balance sheet focuses on the management and use of financial resources.
- While investors and stakeholders may use a balance sheet to predict future performance, past performance is no guarantee of future results.
assets = liabilities + equity
On the other hand, private companies do not need to appeal to shareholders. That is why there is no need to have their financial statements published to the public. Examples of activity ratios are inventory turnover ratio, total assets turnover ratio, fixed assets turnover ratio, and accounts receivables turnover ratio.
Accounting systems or depreciation methods may allow managers to adjust numbers on the balance sheet. Some executives may fiddle with balance sheets to make businesses look more profitable than they actually are. Thus, anyone reading a balance sheet should examine the footnotes in detail to make sure there aren’t any red flags. In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about a business’s balance sheet. Note that in our basic balance sheet template, the “Total Assets” and “Total Liabilities” line items include the values of the “Total Current Assets” and “Total Current Liabilities”, respectively.
Let’s look at each of the balance sheet accounts and how they are reported. Non-current, or long-term, assets, include investments and other less tangible assets which nonetheless can bring value to your business. Take a look at these examples to give you an idea of what to include. Different accounting systems and ways of dealing with depreciation and inventories will also change the figures posted to a balance sheet.
Likewise, its liabilities may include short-term obligations such as accounts payable and wages payable, or long-term liabilities such as bank loans and other debt obligations. And the difference between how much it owns and how much it owes is called owners’ equity. That’s the amount the owners of the company (i.e. shareholders) have invested in the company. But now you’ve got some money to invest, you’re looking at a few companies and trying to figure out whether their shares are worth purchasing.
